Optimization of green LC-MS method for rosuvastatin and teneligliptin using AQbD chemometric approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i5.1415Keywords:
AQbD, Box-Behnken model, green assessment, ICH Guidelines, LC-MS, Method developmentAbstract
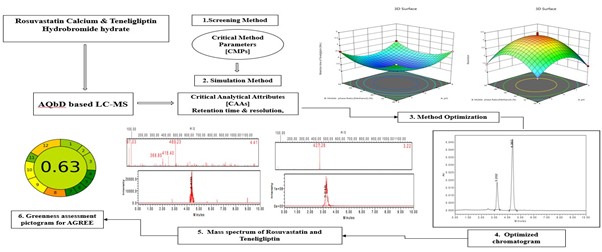
Background: Rosuvastatin combined with Teneligliptin formulation is commonly used in the treatment of Diabetic dyslipidaemia. However, only a few analytical methods have been published for the examination of this drug in a synthetic mixture or in a pharmaceutical dosage form. This study demonstrates the successful application of AQbD principles in developing a reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly LC-MS method. Methodology: Box-Behnken Model: Design of experiment (DoE) strategy to identify and optimize critical method parameters using systematic risk assessment. Methanol: 10mM potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate [pH:6.0] (35:65v/v) was the mobile phase employed in the final optimized LC method, and this was using a Waters LC Xbridge C18 Column 5µm (4.6x250mm) as the stationary phase. The experiment was conducted at a flow rate of 1 mL/min, with a 10 µL injection volume, and an ESI-MS-QDA Detector for detection. An analytical method for validation was applied in accordance with ICH Q2 (R1) guidelines. Results and Discussion: The retention times of Rosuvastatin and Teneligliptin were observed at 4.392 and 3.202 minutes, respectively. The optimized technique showed excellent linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness. Additionally, AGREE metrics and AES were used for assessing the eco-friendly nature of the developed method. Conclusion: The combination of green principles with AQbD experimental design ensures the robustness of the method. This combined framework is used for the first time in method development for the analysis of rosuvastatin with teneligliptin in formulations. Based on the above facts, an economical, robust, and time-saving method has been developed for assessing the quality control of rosuvastatin with teneligliptin in both pharmaceutical and pure forms.
Downloads
References
Ira J G. Diabetic Dyslipidemia: Causes and Consequences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab., 86(3), 965–97 (2001) https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.3.7304
Dhoru MM, Parikh MP, Detholia KK, Patel PJ. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of rosuvastatin and teneligliptin in their synthetic mixture. Indian Drugs., 60(2), 60–69 (2023) https://doi.org/10.53879/id.60.02.13015
Moghadasian MH. Clinical pharmacology of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Life Sci., 65(13), 1329–37 (1999) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(99)00199-X[10]
Lennernas H, Fager G. Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Similarities and differences. Clin Pharmacokinet., 32(5), 403–25 (1997) https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199732050-00005
Rathinam S. Analytical quality by design approach for estimating rosuvastatin calcium in pharmaceutical formulation by green HPLC method : Ecologically evaluated and stability-indicating. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci., 11, 150–60 (2021) https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2021.1101119
Kishimoto M. Teneligliptin: a DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes., 6, 187–95 (2013) https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S35682
Maruthi R, Chandan RS, Barath M, Datta GN, D MM, M MKK, Ahmad F, R MG. Analytical Method development and Validation of Teneligliptin. Research J. Pharm. and Tech ., 13, 4035–40 (2020) https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2020.00713.1
Dharuman N, Lakshmi KS, Krishnan M. Environmental benign RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of anti-hypertensive drugs using analytical quality by design. Green Chem Lett Rev., 16(1), 2214176 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2023.2214176
Park G, Kim M K, Go SH, Choi M, Jang YP. Analytical Quality by Design (AQbD) Approach to the Development of Analytical Procedures for Medicinal Plants. Plants (Basel)., 11(21), 2960 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212960
Keith LH, Gron LU, Young JL. Green analytical methodologies. Chem Rev., 107(6), 2695–2708 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068359e
Kannaiah KP, Sugumaran A, Chanduluru HK, Rathinam S. Environmental impact of greenness assessment tools in liquid chromatography—A review. Microchem J., 170(3), 106685 (2021) http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106685
Płotka-Wasylka J. A new tool for the evaluation of the analytical procedure: Green analytical procedure index. Talanta., 181, 204–209 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.01.013
Gałuszka A, Konieczka P, Migaszewski ZM, Namiesnik J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal Chem., 37, 61–72 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.03.013
Pena-Pereira F, Wojnowski W, Tobiszewski M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness metric approach and software. Anal Chem., 92(14), 10076–10082 (2020) https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01887
Chanduluru HK, Sugumaran A. Estimation of Pitavastatin and Ezetimibe Using UPLC by a Combined Approach of Analytical Quality by Design with Green Analytical Technique. Acta Chromatogr., 34(3), 361–372 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1556/1326.2021.00949
Ghongade AM, Barot ST. Development and validation of stability indicating RP-HPLC method for nebivolol by using the DOE approach. J Appl Pharm Res., 13 (3), 179–91 (2025) https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i3.1062
Mandale DA, Shah C, Jatt R. Development and validation of novel RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of Rosuvastatin and Teneligliptin in bulk and in synthetic mixture. Int J Pharm Res., 13(3), 498–506 (2021) https://doi.org/10.31838/ijpr/2021.13.03.061
Vyas AJ, Parmar K, Katpara B, Zinzala R, Trivedi DR. RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation for Simultaneous Estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium and Teneligliptin hydrobromide hydrate in Synthetic Mixture. Res J Pharm Technol., 17(9), 4325–4328 (2024) https://doi.org/10.52711/0974-360X.2024.00668
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 S R Aswathy, Hemnath Elango

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















