Formulation and optimization of metformin-berberine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for their neuroprotective effects in the brain
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i5.1356Keywords:
Type 2 Diabetes, Solid lipid Nanoparticles, Box Behnken, Optimization, Oxidative stressAbstract
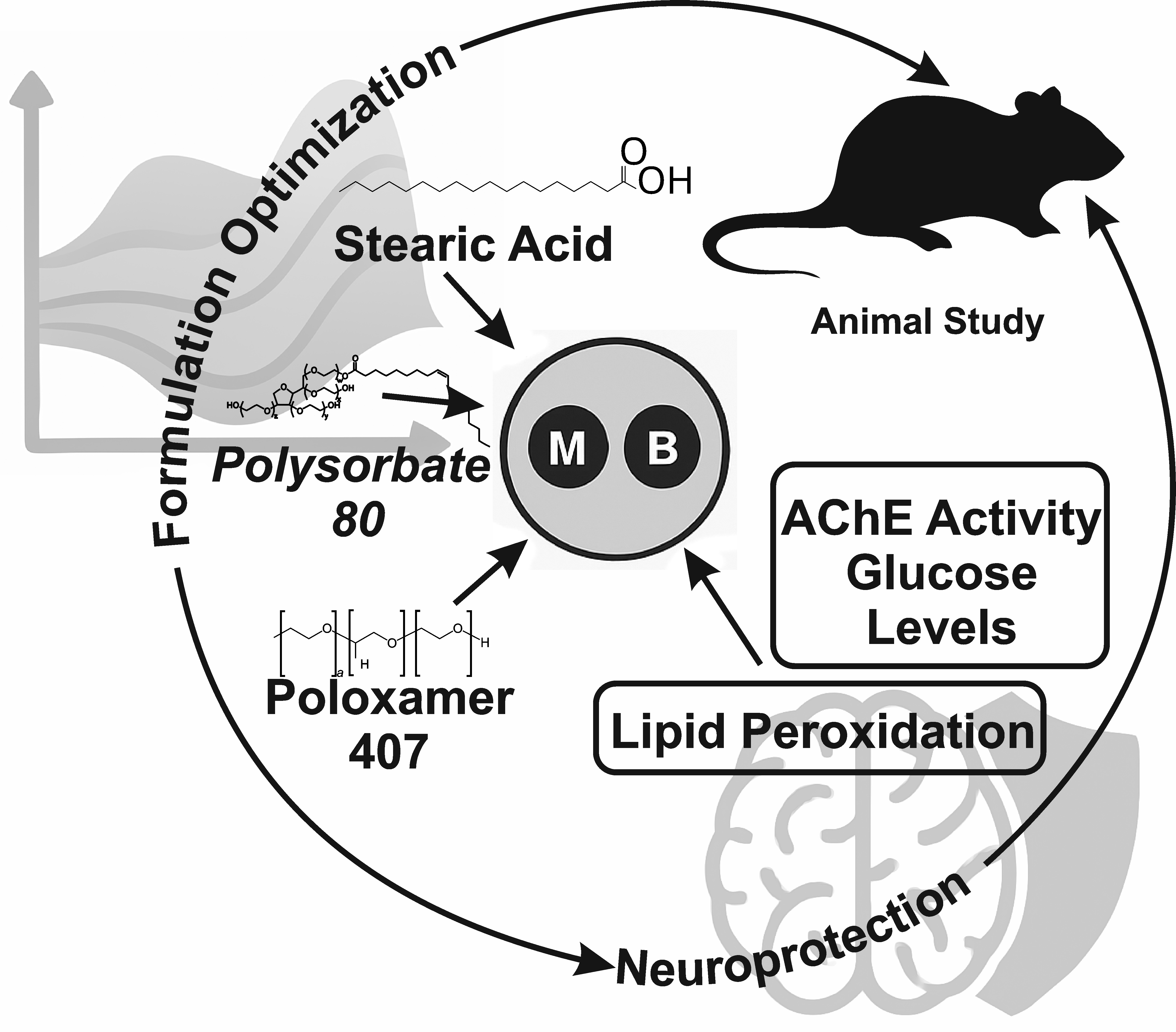
Background: The increasing prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is associated with a heightened risk of developing Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), highlighting the need for effective therapeutic strategies that address the shared pathophysiological mechanisms in both conditions. Methodology: The Metformin-Berberine loaded solid lipid particles (MBSLNs) were prepared by dispersion of different concentrations of stearic acid, polysorbate 80, poloxamer 407, sesame oil, metformin, and berberine. Factor screening studies have been done to identify the influential components. An optimization study was then conducted using a three-factor Box-Behnken design with Design-Expert software. In-Vivo studies confirmed the neuroprotective role of SLNs. Results: The optimized concentrations of the variable factors were determined using the overlay plot generated by the software, resulting in stearic acid (4.84%), polysorbate 80 (1.50%), Poloxamer 407 (1%), and sesame oil (0.31%). The responses, particle size (10–200 nm), zeta potential (> ±30 mV), and polydispersity index (PDI) (0–1) were achieved within the desired range. Discussion: The closeness in experimental and predicted values confirms the reliability of the optimization technique. The optimized formulation exhibits a significant reduction in oxidative stress, and decreased glucose levels were observed when compared to the control, indicating a neuroprotective effect of the formulation. Conclusion: The optimized MBSLNs were affected by the independent parameters examined, including stearic acid, polysorbate 80, Poloxamer 407, and sesame oil concentrations, with significant effects on particle size, zeta potential, and size distribution. The utilization of MBSLNs has emerged as a remarkably effective strategy for enhancing the biological activity of Metformin and berberine in treating T2DM-induced AD.
Downloads
References
Butterfield DA, Di Domenico F, Barone E. Elevated risk of type 2 diabetes for development of Alzheimer disease: a key role for oxidative stress in brain. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease, 1842(9), 1693-706 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.06.010.
Liu S, Liu T, Li J, Hong J, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Wei J. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Exacerbates Pathological Processes of Parkinson's Disease: Insights from Signaling Pathways Mediated by Insulin Receptors. Neurosci Bull, 41(4), 676-690 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-024-01342-8.
Dave BP, Shah YB, Maheshwari KG, Mansuri KA, Prajapati BS, Postwala HI, Chorawala MR. Pathophysiological aspects and therapeutic armamentarium of Alzheimer’s disease: recent trends and future development. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 43(8), 3847-84 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01408-7.
Kciuk M, Kruczkowska W, Gałęziewska J, Wanke K, Kałuzińska-Kołat Ż, Aleksandrowicz M, Kontek R. Alzheimer’s Disease as Type 3 Diabetes: Understanding the Link and Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(22), 11955 (2024) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252211955.
Zhao WQ, Townsend M. Insulin resistance and amyloidogenesis as common molecular foundation for type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)- Molecular Basis of Disease, 1792(5), 482-96 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.10.014.
Zhao WQ, Chen H, Quon MJ, Alkon DL. Insulin and the insulin receptor in experimental models of learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol, 490(1-3), 71-81 (2004) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.02.045.
Abdalla MM. Insulin resistance as the molecular link between diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. World Journal of Diabetes, 15(7), 1430 (2024) https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i7.1430.
Affuso F, Micillo F, Fazio S. Insulin Resistance, a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathological Mechanisms and a New Proposal for a Preventive Therapeutic Approach. Biomedicines, 12(8), 1888 (2024) https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081888.
Lv Z, Guo Y. Metformin and Its Benefits for Various Diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 11, 191 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00191.
Triggle CR, Mohammed I, Bshesh K, Marei I, Ye K, Ding H, MacDonald R, Hollenberg MD, Hill MA. Metformin: Is it a drug for all reasons and diseases? Metabolism, 133, 155223 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155223.
Ekor M. The growing use of herbal medicines: issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front Pharmacol, 4, 177 (2014) https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00177.
Liu D, Meng X, Wu D, Qiu Z, Luo H. A Natural Isoquinoline Alkaloid with Antitumor Activity: Studies of the Biological Activities of Berberine. Front Pharmacol, 10, 9 (2019) https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00009.
Tian E, Sharma G, Dai C. Neuroprotective Properties of Berberine: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Antioxidants (Basel), 12(10), 1883 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12101883.
Wang H, Zhu C, Ying Y, Luo L, Huang D, Luo Z. Metformin and berberine, two versatile drugs in treatment of common metabolic diseases. Oncotarget, 9(11), 10135-10146 (2017) https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20807.
Lyu Y, Li D, Yuan X, Li Z, Zhang J, Ming X, Shaw PC, Zhang C, Kong AP, Zuo Z. Effects of combination treatment with metformin and berberine on hypoglycemic activity and gut microbiota modulation in db/db mice. Phytomedicine, 101, 154099 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154099.
Hao Y, Li J, Yue S, Wang S, Hu S, Li B. Neuroprotective effect and possible mechanisms of berberine in diabetes-related cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 13, 917375 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.917375.
Kodi T, Praveen S, Paka SK, Sankhe R, Gopinathan A, Krishnadas N, Kishore A. Neuroprotective Effects of Metformin and Berberine in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sickness-Like Behaviour in Mice. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci., 2024, 8599268 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/8599268.
Bukke SP, Venkatesh C, Bandenahalli Rajanna S, Saraswathi TS, Kusuma PK, Goruntla N, Balasuramanyam N, Munishamireddy S. Solid lipid nanocarriers for drug delivery: design innovations and characterization strategies—a comprehensive review. Discover applied sciences, 6(6), 279 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-024-05897-z.
Al-Hazmi GA, Elsayed NH, Alnawmasi JS, Alomari KB, Alessa AH, Alshareef SA, El-Bindary AA. Elimination of Ni (II) from wastewater using metal-organic frameworks and activated algae encapsulated in chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel beads: Adsorption isotherm, kinetic, and optimizing via Box-Behnken design optimization. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 299, 140019 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140019.
Baltz N, Scherließ R. Entrapment efficiency methodology for lipid nanoparticles–a literature review. OpenNano, 100251 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onano.2025.100251.
Baek JS, Cho CW. Surface modification of solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of curcumin: Improvement of bioavailability through enhanced cellular uptake, and lymphatic uptake. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 132-140 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.04.013.
Kamarudin NB, Sharma S, Gupta A, Kee CG, Chik SMSBT, Gupta R. Statistical investigation of extraction parameters of keratin from chicken feather using Design-Expert. 3 Biotech, 7, 1–9 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0767-9.
Ferreira SC, Bruns RE, Ferreira HS, Matos GD, David JM, Brandão GC, da Silva EP, Portugal LA, Dos Reis PS, Souza AS, Dos Santos WN. Box-Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Analytica chimica acta, 597(2), 179-86 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.07.011.
Sopyan IY, Gozali DO, Kurniawansyah IS, Guntina RK. Design-expert software (DOE): An application tool for optimization in pharmaceutical preparations formulation. International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics, 14(4), 55-63 (2022) https://doi.org/10.22159/ijap.2022v14i4.45144.
Maran JP, Manikandan S. Response surface modeling and optimization of process parameters for aqueous extraction of pigments from prickly pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) fruit. Dyes and Pigments, 95(3), 465-72 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2012.06.007.
Jakhmola Mani R, Dogra N, Katare DP. The connection between chronic liver damage and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: evidence and insights from a rat model. Brain Sciences, 13(10), 139 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101391.
Knezovic A, Hosch M, Hamann CS, Popp S, Ortega G, Osmanovic-Barilar J, Grünblatt E, Monoranu C, Riederer P, Salkovic-Petrisic M, Schmitt-Böhrer A. Approaching therapy of Alzheimer’s disease via the antidiabetic drug liraglutide—a study with streptozotocin intracerebroventricularly treated Wistar rats. Journal of Neural Transmission, 1-22 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-025-02979-z.
Owumi S, Chimezie J, Salami MO, Ishaya JA, Onyemuwa CV, Nnamdi M, Owoeye O. Lutein and Zeaxanthin abated neurobehavioral, neurochemical and oxido-inflammatory derangement in rats intoxicated with Aflatoxin B1. Toxicon, 258, 108345 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2025.108345.
Sharma AK, Kumar A, Kumar S, Mukherjee S, Nagpal D, Nagaich U, Rajput SK. Preparation and therapeutic evolution of Ficus benjamina solid lipid nanoparticles against alcohol abuse/antabuse induced hepatotoxicity and cardio-renal injury. RSC advance, 7(57), 35938-49 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA04866A.
Prokić M, Borković-Mitić S, Krizmanić I, Gavrić J, Despotović S, Gavrilović B, Radovanović T, Pavlović S, Saičić Z. Comparative study of oxidative stress parameters and acetylcholinesterase activity in the liver of Pelophylax esculentus complex frogs. Saudi J Biol Sci, 24(1), 51-58 (2017)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.09.003.
Kumari N, Mittal A, Rana A, Sharma AK. Callistemon viminalis extracts: dual action on anxiety and neuroprotection via neuroinflammatory and serotonergic pathways. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 55(1), 61-73 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-024-01748-x.
Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol, 7, 88–95 (1961) https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9.
Chigurupati S, Alharbi NA, Sharma AK, Alhowail A, Vardharajula VR, Vijayabalan S, Das S, Kauser F, Amin E. Pharmacological and pharmacognostical valuation of Canna indica leaves extract by quantifying safety profile and neuroprotective potential. Saudi journal of biological sciences, 28(10), 5579-84 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.05.072.
Rani A, Sharma PB, Bhatia S, Sharma AK. Comprehensive study on pharmacognostic, pharmacological, and toxicological features of Ficus racemosa in Alzheimer’s disease using GC–MS and molecular docking analyses. Toxicology Research, 13(4), tfae098 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1093/toxres/tfae098.
Basak, A. Development of rapid and inexpensive plasma glucose estimation by two-point kinetic method based on glucose oxidase-peroxidase enzymes. Indian J. Clin. Biochem, 22, 156–160 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912902.
Wright, J.R.; Colby, H.D.; Miles, P.R. Cytosolic factors which affect microsomal lipid peroxidation in lung and liver. Arch. Biochem. Biophys, 206, 296–304 (1981) https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(81)90095-3.
Kumar AS, Pandit VI, Nagaich UP. Preparation and evaluation of copper nanoparticles loaded with hydrogel for burns. Int J App Pharm, 13(2),108-89 (2021) https://doi.org/10.22159/ijap.2021v13i2.40558.
Johnson L, Gray DM, Niezabitowska E, McDonald TO. Multi-stimuli-responsive aggregation of nanoparticles driven by the manipulation of colloidal stability. Nanoscale, 13(17), 7879-96 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR01190A.
Öztürk K, Kaplan M, Çalış S. Effects of nanoparticle size, shape, and zeta potential on drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 124799 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124799.
Usui S, Healy TW. Zeta potential of stearic acid monolayer at the air–aqueous solution interface. Journal of colloid and interface science, 250(2), 371-8 (2002) https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8340.
Babayevska N, Przysiecka Ł, Iatsunskyi I, Nowaczyk G, Jarek M, Janiszewska E, Jurga S. ZnO size and shape effect on antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity profile. Sci Rep, 12(1), 8148 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12134-3.
Bhatia S, Bhatia S. Nanoparticles types, classification, characterization, fabrication methods and drug delivery applications. Natural polymer drug delivery systems: Nanoparticles, plants, and algae, 33-93 (2016) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41129-3_2.
Rizvi SAA, Saleh AM. Applications of nanoparticle systems in drug delivery technology. Saudi Pharm J., 26(1), 64-70 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2017.10.012.
Song T, Gao F, Guo S, Zhang Y, Li S, You H, Du Y. A review of the role and mechanism of surfactants in the morphology control of metal nanoparticles. Nanoscale, 13(7), 3895-910 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR07339C.
Ignjatović J, Đuriš J, Cvijić S, Dobričić V, Montepietra A, Lombardi C, Ibrić S, Rossi A. Development of solid lipid microparticles by melt-emulsification/spray-drying processes as carriers for pulmonary drug delivery. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 156, 105588 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105588.
Sambhakar S, Saharan R, Narwal S, Malik R, Gahlot V, Khalid A, Najmi A, Zoghebi K, Halawi MA, Albratty M, Mohan S. Exploring LIPIDs for their potential to improves bioavailability of lipophilic drugs candidates: A review. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 31(12), 101870 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101870.
Walia N, Zhang S, Wismer W, Chen L. A low energy approach to develop nanoemulsion by combining pea protein and Tween 80 and its application for vitamin D delivery. Food Hydrocolloids for Health, 2, 0007 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fhfh.2022.100078.
Aldayel TS, Badran MM, Alomrani AH, AlFaris NA, Altamimi JZ, Alqahtani AS, Nasr FA, Ghaffar S, Orfali R. Optimization of cationic nanoparticles stabilized by Poloxamer 407 188: A potential approach for improving the biological activity of Aloe perryi. Heliyon, 9(12) (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22691.
Abourehab MAS, Khames A, Genedy S, Mostafa S, Khaleel MA, Omar MM, El Sisi AM. Sesame Oil-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Nicergoline, Intranasal Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Synergistic Cerebrovascular Protection. Pharmaceutics ,13(4), 581 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040581.
Sharma S, Zhang Y, Akter KA, Nozohouri S, Archie SR, Patel D, Villalba H, Abbruscato T. Permeability of Metformin across an In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model during Normoxia and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation Conditions: Role of Organic Cation Transporters (Octs). Pharmaceutics, 15(5), 1357 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051357.
Wu X, Liu X, Yang L, Wang Y. Berberine Protects against Neurological Impairments and Blood-Brain Barrier Injury in Mouse Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neuroimmunomodulation, 29(4), 317-326 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1159/000520747.
Kreuter J, Shamenkov D, Petrov V, Ramge P, Cychutek K, Koch-Brandt C, Alyautdin R. Apolipoprotein-mediated transport of nanoparticle-bound drugs across the blood-brain barrier. J Drug Target, 10(4), 317-25 (2002) https://doi.org/10.1080/10611860290031877.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Ravina Yadav, Ruchi Jakhmola Mani, Arun Sharma, Ashish Kumar, Deepshikha Katare

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















