Innovative nanostructured lipid carrier gel for enhanced topical delivery of roflumilast in psoriasis management
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i4.1242Keywords:
Nanostructured lipid carriers, Roflumilast, Psoriasis, Topical drug delivery, Controlled releaseAbstract
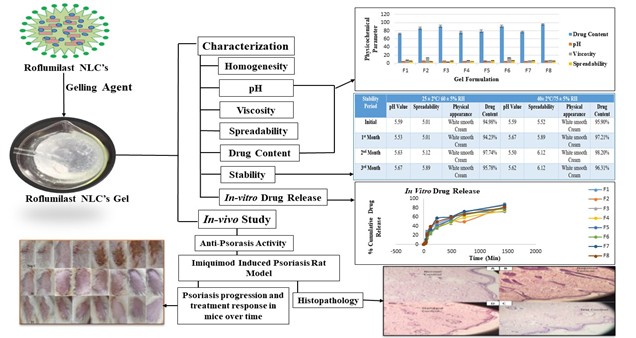
Background: Psoriasis is a chronic immune-mediated skin disorder marked by keratinocyte hyperproliferation, inflammation, and oxidative stress, causing erythematous, scaly plaques that impair quality of life. Current therapies have side effects and poor solubility, highlighting the need for improved topical delivery systems. Methodology: An NLC-based gel encapsulating the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast was developed for enhanced topical delivery. NLCs were prepared by high-pressure homogenization with oleic acid, glycerol monostearate, and Tween 80, and incorporated into a Carbopol 934 gel. The physicochemical properties, encapsulation efficiency, in vitro release, and in vivo efficacy of imiquimod in imiquimod-induced psoriatic rats were evaluated. Results: The developed gel was homogeneous, white, and transparent, with a dermally compatible pH (5.36-5.85), optimal viscosity (3.5-14.5 Pa·s), and good spreadability (4.3-7.2 g/cm/s). Formulation F3 showed high encapsulation efficiency (90.38 ± 2.91%) and sustained drug release (~90% over 24 hours). Drug content ranged from 72% to 95%. Ex vivo skin permeation studies demonstrated enhanced roflumilast penetration. In vivo application led to a significant reduction in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores from 6.5 on Day 1 to 1.6 on Day 9. No signs of erythema, edema, or rashes were observed during the 72-hour skin irritation study, confirming excellent dermal compatibility. Histopathology confirmed decreased inflammation, reduced hyperkeratosis, and restored epidermal architecture. Discussion: The NLC-based roflumilast gel showed favorable physicochemical and biopharmaceutical properties, offering improved delivery and sustained release over conventional psoriasis therapies. Conclusion: Roflumilast-NLC gel is a promising topical therapy for psoriasis with controlled release and enhanced skin retention.
Downloads
References
Bakshi H, Nagpal M, Singh M, Dhingra GA, Aggarwal G. Treatment of psoriasis: a comprehensive review of entire therapies. Current drug safety, 15, 82–104 (2020) https://doi.org/10.2174/1574886315666200128095958.
Lebwohl MG, Papp KA, Stein Gold L, Gooderham MJ, Kircik LH, Draelos ZD, Kempers SE, Zirwas M, Smith K, Osborne DW. Trial of roflumilast cream for chronic plaque psoriasis. New England Journal of Medicine, 383, 229–39 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2000073.
Schafer PH, Parton A, Capone L, Cedzik D, Brady H, Evans JF, Man H-W, Muller GW, Stirling DI, Chopra R. Apremilast is a selective PDE4 inhibitor with regulatory effects on innate immunity. Cell Signal, 26, 2016–29 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.05.014.
Singh A, Kumar P, Sharma H. Breakthrough Opportunities of Nanotheranostics in Psoriasis: From Pathogenesis to Management Strategy. Infectious Disorders - Drug Targets, 25, (2025) https://doi.org/10.2174/0118715265298802240603120251.
Card GL, England BP, Suzuki Y, Fong D, Powell B, Lee B, Luu C, Tabrizizad M, Gillette S, Ibrahim PN. Structural basis for the activity of drugs that inhibit phosphodiesterases. Structure, 12, 2233–47 (2004) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.10.004.
Moustafa F, Feldman SR. A review of phosphodiesterase-inhibition and the potential role for phosphodiesterase 4-inhibitors in clinical dermatology. Dermatol Online J, 20, (2014) https://doi.org/10.5070/D3205022608.
Zhang X, Xing H, Zhao Y, Ma Z. Pharmaceutical dispersion techniques for dissolution and bioavailability enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Pharmaceutics, 10, 74 (2018) https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030074.
Huang Y, Dai W-G. Fundamental aspects of solid dispersion technology for poorly soluble drugs. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 4, 18–25 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2013.11.001.
Bachhav AA, Pingale PL, Upasani CD. Pharmaceutical development of etodolac transfersomal gel for topical drug delivery system in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Appl. Pharm. Res., 12, 155–70 (2024) https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v12i4.597.
Singh A, Kumar P, Verma A. Development and Optimization of Roflumilast-loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLCs) Formulation for Topical Delivery. Oriental Journal Of Chemistry, 41, 11–24 (2025) https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/410102.
Waghule T, Rapalli VK, Singhvi G, Manchanda P, Hans N, Dubey SK, Hasnain MS, Nayak AK. Voriconazole loaded nanostructured lipid carriers based topical delivery system: QbD based designing, characterization, in-vitro and ex-vivo evaluation. Journal of drug delivery science and technology, 52, 303–15 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.04.026.
Rapalli VK, Kaul V, Waghule T, Gorantla S, Sharma S, Roy A, Dubey SK, Singhvi G. Curcumin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for enhanced skin retained topical delivery: optimization, scale-up, in-vitro characterization and assessment of ex-vivo skin deposition. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 152, 105438 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105438.
Rajalakshmi R, Selvaraj K. Study on Clinical Profile of Scabies and Comparison of Efficacy of Topical Agents in Treatment of Scabies. J. Appl. Pharm. Res., 11, 59–63 (2023) https://doi.org/10.18231/j.joapr.2023.11.5.59.63.
Chaudhary H, Rohilla A, Rathee P, Kumar V. Optimization and formulation design of carbopol loaded Piroxicam gel using novel penetration enhancers. International journal of biological macromolecules, 55, 246–53 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.01.015.
Kakkar V, Kaur IP, Kaur AP, Saini K, Singh KK. Topical delivery of tetrahydrocurcumin lipid nanoparticles effectively inhibits skin inflammation: in vitro and in vivo study. Drug development and industrial pharmacy, 44, 1701–12 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2018.1492607.
Talole S, Godge R, Tambe N, Mhase N. Formulation and optimization of upadacitinib-loaded transdermal patches for rheumatoid arthritis with zero-order release kinetics. J. Appl. Pharm. Res., 13, 181–93 (2025) https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i2.1037.
Mukherjee S, Ash D, Majee SB, Biswas GR. Comparative study of Span 40 and Span 60 based soy-gels for topical drug delivery. Asian J Pharm Clin Res, 12, 259–65 (2019) http://dx.doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2019.v12i6.33554.
Gupta S, Dubey S, Patel SK, Lakra AP, Minz S. Chitosan-coated CMC and carbopol hydrogel beads for controlled release of metformin in diabetes management. J. Appl. Pharm. Res., 13, 73–85 (2025) https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i2.1006.
Taş Ç, Ozkan Y, Savaşer A, Baykara T. In vitro and ex vivo permeation studies of chlorpheniramine maleate gels prepared by carbomer derivatives. Drug development and industrial pharmacy, 30, 637–47 (2004) https://doi.org/10.1081/DDC-120037665.
Baghel S, Nair VS, Pirani A, Sravani AB, Bhemisetty B, Ananthamurthy K, Aranjani JM, Lewis SA. Luliconazole‐loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical treatment of superficial Tinea infections. Dermatologic Therapy, 33, e13959 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.13959.
Parmar KM, Jagtap CS, Katare NT, Dhobi M, Prasad SK. Development of a psoriatic-like skin inflammation rat model using imiquimod as an inducing agent. Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 53, 125 (2021) https://doi.org/10.4103/ijp.IJP_506_19.
Panonnummal R, Sabitha M. Anti-psoriatic and toxicity evaluation of methotrexate loaded chitin nanogel in imiquimod induced mice model. International journal of biological macromolecules, 110, 245–58 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.112.
Negi P, Sharma I, Hemrajani C, Rathore C, Bisht A, Raza K, Katare OP. Thymoquinone-loaded lipid vesicles: A promising nanomedicine for psoriasis. BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 19, 1–9 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2675-5.
Sah SK, Badola A, Nayak BK. Emulgel: Magnifying the application of topical drug delivery. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research, 5, 25–33 (2017) https://doi.org/10.30750/ijpbr.5.1.4
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Abhishek Singh, Anurag Verma, Prashant Kumar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















