Formulation, designing and evaluation of gastro-retentive floating microspheres using silymarin, curcumin and piperine for hepatoprotection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i4.1167Keywords:
Gastro-retentive, Microspheres, Curcumin, Silymarin, Piperine, Ethyl cellulose, HepatoprotectionAbstract
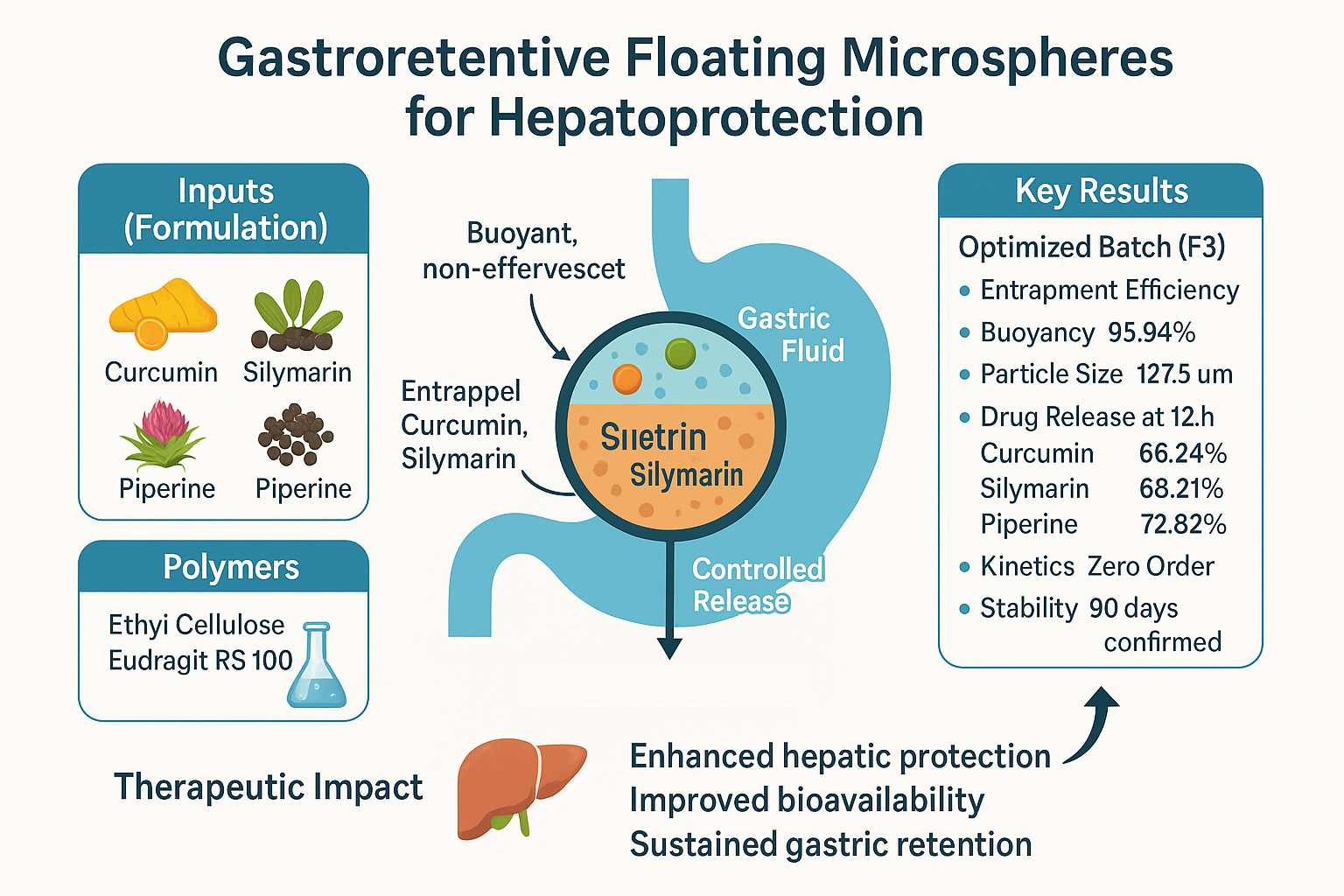
Background: Curcumin, Silymarin, and Piperine are natural phytoconstituents with proven hepatoprotective effects; however, their therapeutic efficacy is limited by poor water solubility and low oral bioavailability. A gastro-retentive floating drug delivery system offers a strategic approach to enhance gastric residence time and improve absorption in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Methodology: Floating microspheres were developed using the solvent evaporation technique with Ethyl Cellulose and Eudragit RS 100 as polymers. A series of trial formulations was statistically optimized using Design Expert® software. The microspheres were evaluated for particle size, buoyancy, entrapment efficiency, drug release profile, and stability. Results and Discussion: The optimized formulation (Batch F3) demonstrated high encapsulation efficiency (>98%) and sustained buoyancy of 95.94% over 8-hour. At the end of 12 hours, cumulative drug release was 66.24% for Curcumin, 68.21% for Silymarin, and 72.82% for Piperine. Drug release followed zero-order kinetics, with the best model fit (R² = 0.9938) observed for Piperine. SEM images confirmed the presence of spherical and uniform microspheres. The formulation remained stable for 90 days under ICH Q1A(R2) conditions. Conclusion: The developed microspheres offer a promising gastroretentive system for controlled delivery of hepatoprotective agents, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes for liver-related disorders.
Downloads
References
Lokhande S. Recent trends in development of gastro-retentive floating drug delivery system: A review. Asian J. Res. Pharm. Sci., 9(2), 91–96 (2019) https://doi.org/10.5958/2231-5659.2019.00014.6.
Sinha S, Thapa S, Singh S, Dutt R, Verma R, Pandey P, Mittal V, Rahman MH, Kaushik D. Development of biocompatible nanoparticles of tizanidine hydrochloride in orodispersible films: in vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation, and cytotoxic study on carcinoma cells. Current Drug Delivery. 2022 Dec 1;19(10):1061-72 https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201819666220321111338.
Luo Q, Ding J, Zhu L, Chen F, Xu L. Hepatoprotective effect of wedelolactone against concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice. Am. J. Chin. Med., 46(4), 819–833 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X1850043X.
Kothawade SN, Chaudhari PD. Development of biodegradable porous starch foam for improving oral delivery of eprosartan mesylate. J of Adv Sci Research. 2021 Sep 30;12(03 Suppl 1):120-6 https://doi.org/10.55218/JASR.s1202112314.
Masood M, Arshad M, Rahmatullah Q et al. Picrorhiza kurroa: An ethnopharmacologically important plant species of Himalayan region. Pure Appl. Biol., 4, 407–417 (2021) http://dx.doi.org/10.19045/bspab.2015.43017.
Kothawade SN, Avhad SR, Rngade RB, Kotkar RS, Sabale SS, Baviskar AK, Gawade MM. Aloe vera powder as a potent bioenhancer: a comprehensive review. Int J Pharm Phytopharmacol Res. 2023 Apr;13(2):37-44 https://doi.org/10.51847/ZFFtdBFaPt.
Kalepu S, Nekkanti V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 2015 Sep 1;5(5):442-53 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.003.
Bhalani DV, Nutan B, Kumar A, Singh Chandel AK. Bioavailability enhancement techniques for poorly aqueous soluble drugs and therapeutics. Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 23;10(9):2055 https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10092055.
Arane PM, Ghanwat DA, Boyane V, Kothawade SN, Doshi P. Preparation and in Vitro Characterization of Eprosartan Mesylate Solid Dispersions using Skimmed Milk Powder as Carrier. Int J of Adv in Pharm Res. 2011 Dec;2(12):658-65 https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.50.3.31.
Gupta R, Chen Y, Xie H. In vitro dissolution considerations associated with nano drug delivery systems. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Nov;13(6):e1732 https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1732.
Shabbir M, Sajid A, Hamid I, Sharif A, Akhtar MF, Raza M, Ahmed S, Peerzada S, Amin MU. Influence of different formulation variables on the performance of transdermal drug delivery system containing tizanidine hydrochloride: in vitro and ex vivo evaluations. Braz J of Pharma Sci. 2019 Apr 8;54:e00130 https://doi.org/10.1590/s2175-97902018000400130.
Kaurav H, Tripathi M, Kaur SD, Bansal A, Kapoor DN, Sheth S. Emerging trends in bilosomes as therapeutic drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 23;16(6):697 https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060697.
Pınar SG, Oktay AN, Karaküçük AE, Çelebi N. Formulation strategies of nanosuspensions for various administration routes. Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 17;15(5):1520 https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051520.
He S, Mu H. Microenvironmental pH modification in buccal/sublingual dosage forms for systemic drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 14;15(2):637 https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020637.
Kallakunta VR, Sarabu S, Bandari S, Tiwari R, Patil H, Repka MA. An update on the contribution of hot‑melt extrusion technology to novel drug delivery in the twenty‑first century: Part I. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019 May;16(5):539‑50 https://doi.org/10.1080/17425247.2019.1609448.
Kapoor DU, Vaishnav DJ, Garg R, et al. Exploring the impact of material selection on the efficacy of hot‑melt extrusion. Int J Pharm. 2025 Jan 5;668:124966 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124966.
Dinesh Kumar. Various Aspects of Solid Dispersion Technology: A Review. Res J Pharm Technol. 2025 Apr;18(4):1872‑8 https://doi.org/10.52711/0974-360X.2025.00267.
Kaurav H, Tripathi M, Kaur SD, Bansal A, Kapoor DN, Sheth S. Emerging trends in bilosomes as therapeutic drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 23;16(6):697 https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060697.
Rampurawala M, Shah C, Upadhyay U. Nano-Suspension: A Novel and Emerging Approach in Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery. Int. J. of Pharm. Sci. 2024;2(9):133-46 https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13629942.
Mura P, Fenyvesi F. Development of Oral Tablets of Nebivolol with Improved Dissolution via Cyclodextrin Complexation. Molecules. 2024 May;29(10):1234 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules290101234.
Smruti PC, Gupte A. Solid Dispersions Obtained by Ball Milling as Delivery Platform for ETD—Improved Solubility and Dissolution. Materials. 2022 Aug;17(16):3923 https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163923.
PDA Technical Report Authors. Hot‑Melt Extrusion: An Emerging Technique for Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water‑Soluble Drugs. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2021 Apr;75(4):357‑65 https://doi.org/10.5731/pdajpst.2019.011403.
Joshi K, Chandra A, Jain K, Talegaonkar S. Nanocrystalization: an emerging technology to enhance the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Pharmaceu Nanotech. 2019 Aug 1;7(4):259-78 https://doi.org/10.2174/2211738507666190405182524.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Misbah Sultana Abdul Kausar Badewale, Varsha Siddheswar Tegeli

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















