Chromatographic profiling of leniolisib impurities using HPLC and LC-MS/MS: degradation behaviour, structural characterization, and in-silico toxicity evaluation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i4.1143Keywords:
Leniolisib, impurities analysis, stress degradation compounds, LC–MS/MS characterization, in-silico studyAbstract
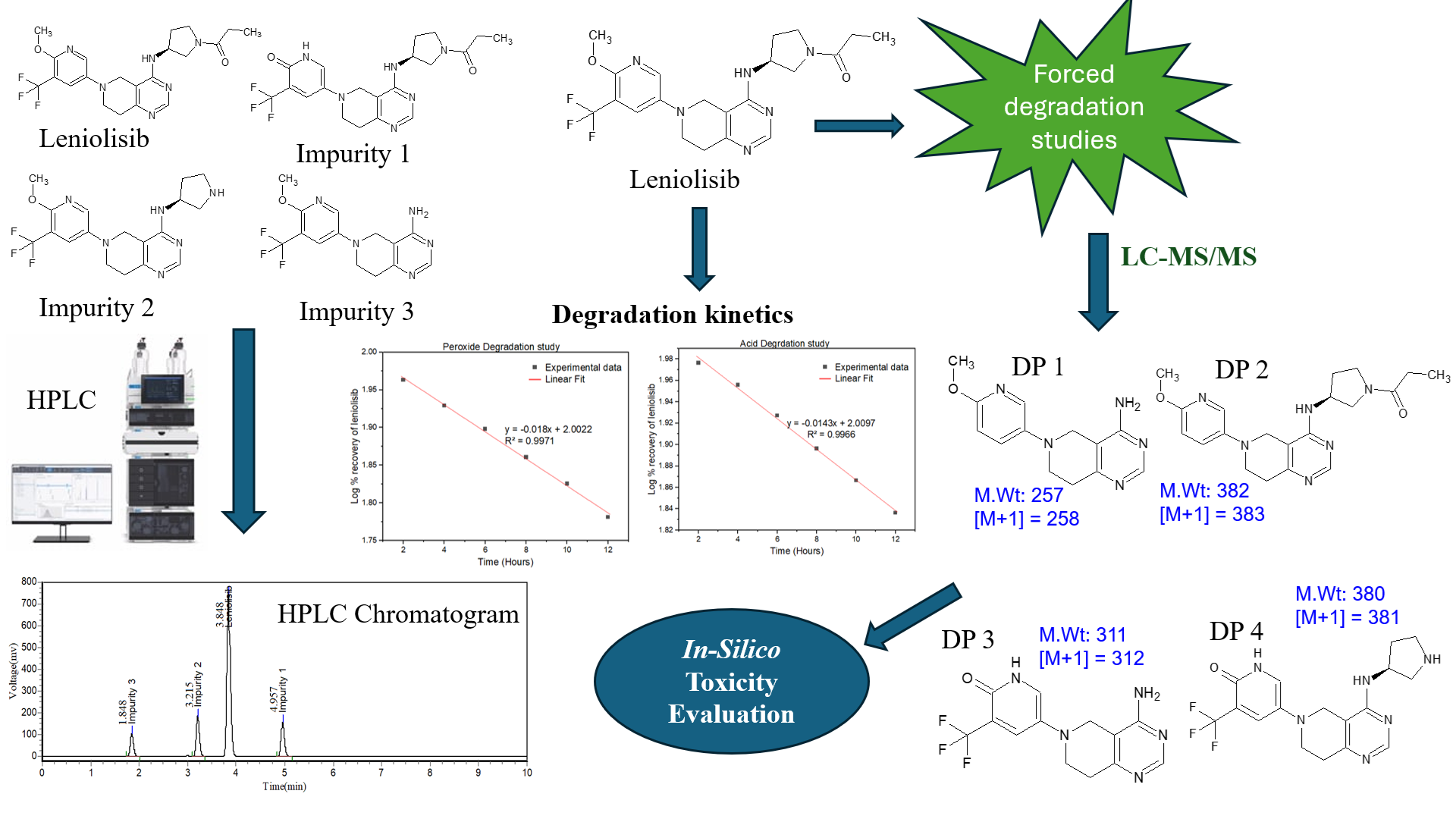
Background: This study presents a comprehensive analytical investigation of leniolisib, focusing on impurity profiling, degradation kinetics, structural characterization, and in silico toxicity prediction of degradation products (DPs). Methodology: A systematic approach was employed to optimize the analytical method for leniolisib and its impurities, along with LC–MS/MS-based identification and in-silico toxicity prediction of DPs. Result and Discussion: Method optimized as Waters Symmetry C18 column and an isocratic mobile phase (methanol: sodium acetate buffer, 55:45 v/v) at 0.90 mL/min with UV detection at 229 nm. Leniolisib was most susceptible to acid and oxidative stress, resulting in 31.24% and 39.58% degradation, respectively. Pseudo-first-order kinetics was observed with rate constants of 0.0329 h⁻¹ (acidic) and 0.0414 h⁻¹ (oxidative), with half life of 21.08 h and 16.73 h. LC–MS/MS elucidates the identities of major DPs that enable the proposed degradation pathways. The MS/MS characterization confirms DP 1 with a formula of C13H15N5O with a mass of 257 g/mol, whereas DP 2, 3, and 4 were identified to have formulas of C20H26N6O2, C13H12F3N5O, and C17H19F3N6O with masses of 382, 311, and 380 g/mol, respectively. The In-silico toxicity predictions show DP 1 (LD₅₀ = 500 mg/kg) and DP 2 (729 mg/kg) as moderate toxicity (class 4), DP 4 shows the least toxicity (class 5, LD₅₀ = 1750 mg/kg), whereas DP3 shows the highest toxicity (class 3, LD₅₀ = 250 mg/kg). Conclusion: The developed method and accompanying data provide a critical foundation for routine quality control, stability testing, and regulatory submissions for leniolisib-based formulations.
Downloads
References
Ravinder Bairam, Hemant Kumar Tatapudi, Vijay Srinivas Pothula, Likhitha Akaram, Sambasiva Rao Tummala, Naveena Gorrepati. Analytical quality by design approach in RP-HPLC method development for the quantification of mirabegron and solifenacin succinate in pharmaceutical formulation, Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience., 14(1), 1-12 (2024) https://doi.org/10.33263/LIANBS141.048
Duggan S, Al-Salama ZT. Leniolisib: First Approval. Drugs. 83(10), 943–948 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-023-01895-
Tummala SR, Amgoth KP. Development of GC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Four Nitrosoamine Genotoxic Impurities in Valsartan. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci., 19 (4), 455-461 (2022) https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.galenos.2021.17702
Rajesh VB, Battula SR, Kapavarapu MVNR, Mandapati VR. A novel Rivaroxaban degradation impurity detection by RP-HPLC extraction by preparative chromatography, and characterization by LC-MS, NMR and FT-IR: Analysis of novel impurity in batch samples and tablets of Rivaroxaban. Rasayan J. Chem., 15, 2373-2381 (2022) https://doi.org/10.31788/RJC.2022.1547008
Singh AK, Carroll K, McMurray JJ, Solomon S, Jha V, Johansen KL, et al. Leniolisib for the Treatment of Anemia in Patients Not Undergoing Dialysis. N Engl J Med., 385(25), 2313–2324 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2113380
Rajesh Varma Bhupatiraju, Bikshal Babu Kasimala, Lavanya Nagamalla, Fathima Sayed. Structural evaluation of degradation products of Loteprednol using LC-MS/MS: Development of an HPLC method for analyzing process-related impurities of Loteprednol. Anal. Sci. Technol., 37(2), 98-113 (2024) https://doi.org/10.5806/AST.2024.37.2.98.
Prasad SS, Kasimala BB, Anna VR. QbD Based Analytical Method Development and Validation for the Separation and Quantification of Agomelatine and Its Impurities in Solid Oral Dosage Forms Using HPLC. Rasayan J. Chem., 14(4), 2183-2190 (2021) http://doi.org/10.31788/RJC.2021.1446426
Panchumarthy Ravi Sankar, Kamma Harsha Sri, Prasada Rao ChV, Kancharla Pujitha. Stability-indicating HPLC Method Development and Validation for Quantitative Analysis of Leniolisib: A Novel Selective PI3K Inhibitor. Pharm. Res.: Recent Adv. Trends., 10(12), 60-87 (2024) https://doi.org/10.9734/bpi/prrat/v10/3310
Rajesh Varma Bhupatiraju, Srinivasa Kumar B, Venkata Swamy Tangeti, Kandula Rekha, Fathima Sayed. LC and LC-MS/MS Studies for Identification and Characterisation of Related Substances and Degradation Products of Abrocitinib. Toxicol. Int., 31(2), 321-334 (2024) https://doi.org/10.18311/ti/2024/v31i2/36370
Amgoth KM, Tummala SR. LC-MS/MS approach for the quantification of five genotoxic nitrosoimpurities in varenicline. J. Res. Pharm., 26(6). 1685-1693 (2022) https://doi.org/10.29228/jrp.259
Satoshi Machino, Yoko Yokoyama, Toyohiro Egawa, Hiroshi Satoh, Katsuhiro Miyajima, Midori Yoshida, Satoshi Asano, Shogo Ozawa. Case analysis of kinetics investigations in toxicity studies of pesticides to identify the nonlinearity of internal exposure and the influences of nonlinearity on the toxicological interpretation of pesticide residue. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 124, 104958 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2021.104958.
Rajesh Varma Bhupatiraju, Pavani Peddi, Subhashini Edla, Kandula Rekha, Bikshal Babu Kasimala. Green Analytical Approach for HPLC Method Development for Quantification of Sorafenib and Its Pharmacopeia Impurities: LC–MS/MS Characterization and Toxicity Prediction of Stress Degradation Products. Sep. Sci. Plus., 7(9), e202400106 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1002/sscp.202400106
Rasheed Babu Shaik, Dharmasoth Rama Devi, Basavaiah K, Rao BM. Isolation, LC–MS/MS, NMR Characterization, In-Silico Toxicity, and ADME Evaluation of Stress-Degradation Products of Sunitinib with Optimized Stability-Indicating HPLC Method for Quantification of Sunitinib and its Impurities. Sep. Sci. Plus., 8, e70001 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1002/sscp.70001
Bhangare D, Rajput N, Jadav T. et al. Systematic strategies for degradation kinetic study of pharmaceuticals: an issue of utmost importance concerning current stability analysis practices. J. Anal. Sci. Technol., 13, 7 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-022-00317-6
Tummala SR, Gorrepati N, Tatapudi HK. Head Space GC-MS/MS Method for Quantification of Five Nitrosoamine-Genotoxic Impurities in Metformin HCl. Current Pharmaceutical Analysis. 20(8), 944 – 952 (2024) https://doi.org/10.2174/0115734129332940240919113159
Aboras SI, Megahed AA, El-Yazbi F. et al. White targeted chromatographic screening method of Molnupiravir and its metabolite with degradation kinetics characterization and in-silico toxicity. Sci Rep., 13, 17919 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-44756-6
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Rahul Gunupati, S. Lakshmi Tulasi, Rasheed Babu Shaik, L. Bhagya Lakshmi, Venkata Swamy Tangeti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















