RP-HPLC method for quantitative estimation of naftifine hydrochloride in formulated products: development and validation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i4.1115Keywords:
Naftifine hydrochloride, reversed-phase HPLC, validation, pharmaceutical, topical antifungalAbstract
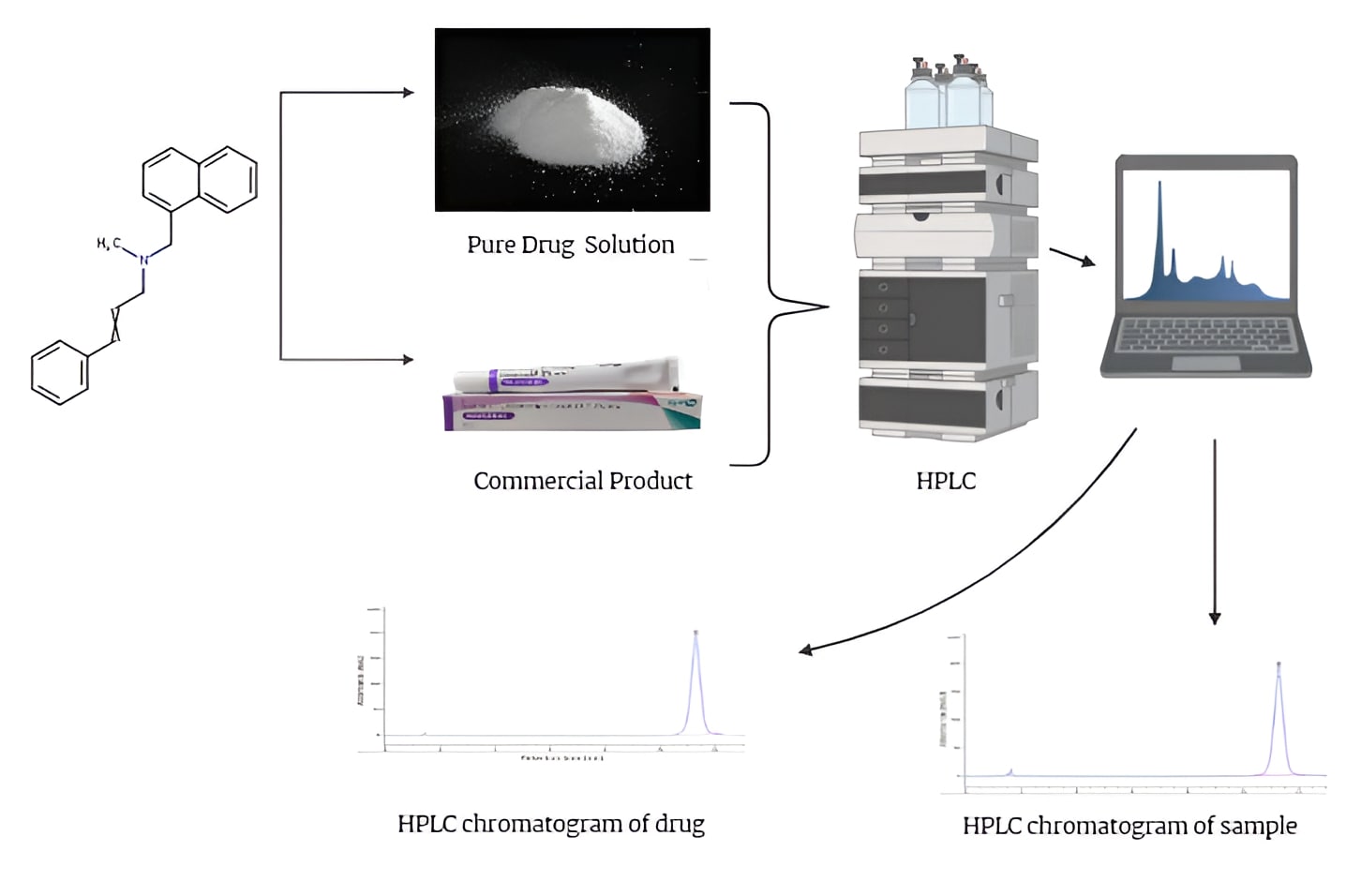
Background: Naftifine hydrochloride is an allylamine antifungal agent commonly used to treat dermatophyte infections. It inhibits squalene epoxidase, a key enzyme in ergosterol biosynthesis, thereby disrupting the integrity of the fungal cell membrane. It exhibits broad-spectrum activity against dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds, and is typically formulated as a 1% topical cream or gel. Methodology: A rapid and robust reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method was developed and validated for the estimation of naftifine hydrochloride in a topical cream formulation (2% Naftifast, Zydus), in accordance with ICH and FDA guidelines. Chromatographic separation was achieved on an Inertsil ODS column using an isocratic mobile phase consisting of 35% acetonitrile, 40% methanol, 25% water, and 0.8% triethylamine (pH adjusted to 5.5 with acetic acid) at a flow rate of 1.4 mL/min. Detection was performed at 265 nm. Results and Discussion: Naftifine hydrochloride showed a retention time of approximately 4.0 minutes with a total run time of 6.0 minutes. The method displayed excellent linearity over a concentration range of 20–120 µg/mL (R² > 0.999). Recovery studies indicated a mean recovery of 100.4%. Precision was confirmed by relative standard deviation (RSD) values of less than 2%, demonstrating the method’s reproducibility. Conclusion: The proposed RP-HPLC method is simple, precise, and time-efficient. It is suitable for routine quality control of naftifine hydrochloride in pharmaceutical dosage forms due to its short analysis time and strong validation performance.
Downloads
References
Rayens E, Norris KA. Prevalence and healthcare burden of fungal infections in the United States, 2018. Open Forum Infect. Dis., 9 (1), ofab593 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab593.
Reddy GKK, Padmavathi AR, Nancharaiah YV. Fungal infections: pathogenesis, antifungals and alternate treatment approaches. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci., 3, 100137 (2022)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmicr.2022.100137.
Rodrigues ML, Nosanchuk JD. Fungal diseases as neglected pathogens: a wake-up call to public health officials. In: Advances in Clinical Immunology, Medical Microbiology, COVID-19, and Big Data. Jenny Stanford Publishing, Singapore, pp. 399–411 (2021).
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Naftin (naftifine hydrochloride) gel. Prescribing Information (2020). Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/204286s004lbl.pdf (Accessed 25 Aug 2025).
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Naftin (naftifine hydrochloride) topical. Prescribing Information (2018). Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/019356s008,019599s014,204286s003lbl.pdf (Accessed 25 Aug 2025).
International Council for Harmonisation (ICH). Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1). ICH, Geneva (2005).
Ahmed N, Prajapati V, Mishra P, Mishra NT. Dosage form design: from concept to compliance—navigating regulatory standards and patient needs. Int. J. Drug Regul. Aff., 12 (1), 24–35 (2024) https://doi.org/10.22270/ijdra.v12i1.647.
Sharma S, Singh N, Ankalgi AD, Rana A, Ashawat MS. Modern trends in analytical techniques for method development and validation of pharmaceuticals: a review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther., 11(1-s), 121–130 (2021) https://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v11i1-s.4515.
Anlay DZ, Paque K, Van Leeuwen E, Cohen J, Dilles T. Tools and guidelines to assess the appropriateness of medication and aid deprescribing: an umbrella review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 90 (1), 12–26 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.15708.
Lotfy HM, Genc AA, Bay M, Tiris G, Obaydo RH, Erk N. Development of eco-friendly sensitive HPLC method for determination of letrozole and assessment of validation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem., 158, 116926 (2025)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.talo.2025.100425.
Jandera P, Churáček J. Liquid chromatography with programmed composition of the mobile phase. In: Advances in Chromatography. CRC Press; 2021: 125–260.
Esentürk İ, Balkan T, Güngör S, Saraç S, Erdal MS. Preparation and characterization of naftifine-loaded poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate electrospun nanofibers. Braz J Pharm Sci., 56, e18440 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1590/s2175-97902019000318440.
Riley CM, Nguyen KL, editors. Specification of Drug Substances and Products: Development and Validation of Analytical Methods. Elsevier; 2024.
Elumalai S, Dantinapalli VL, Palanisamy M. Comparative analysis of analytical method validation requirements across ICH, USP, ChP and ANVISA: a review. J Pharm Res Int., 36 (12), 54–71 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.9734/jpri/2024/v36i127628.
Ooha P, Latha PM, Devi PU. Method development and validation for the simultaneous estimation of pancreatin and activated dimethicone in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms by RP-HPLC. J Transl Res Life Sci., 1(5), 11–23 (2025) http://dx.doi.org/10.71223/q1cd2993.
Kulkarni M, More P. Development and validation of an HPLC–PDA method for quantitation of metronidazole in finished drug formulation. Discov Chem., 2 (1), 1–21 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1007/s44371-025-00109-y.
Bhujbal S, Rupenthal ID, Agarwal P. Development and validation of a stability-indicating HPLC method for assay of tonabersat in pharmaceutical formulations. Methods., 231, 178–185 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.10.001.
Blessy M, Patel RD, Prajapati PN, Agrawal YK. Development of forced degradation and stability indicating studies of drugs: a review. J Pharm Anal., 4 (3), 159–165 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2013.09.003.
Kang NW, Lee JY, Song K, Kim MH, Yoon S, Nguyen DT, et al. Development and validation of liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for pharmacokinetic evaluation of 7β-(3-ethyl-cis-crotonoyloxy)-1α-(2-methylbutyryloxy)-3,14-dehydro-Z-notonipetranon in rats. Molecules., 25 (8), 1774 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081774.
Ranganath MK, Sudha PC, Ramesh G, Abishek T, Baskaran V, Kumar RH, Dang R. Method development and validation of antihypertensive drugs using HPLC technique. Indian J Pharm Educ Res., 58 (3s), s1053–s1061 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.58.3s.105.
Khairy MA, Hamad A, Hamed M, Locatelli M, Mansour FR. A stability-indicating RP-HPLC–UV assay method for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone, tretinoin, hydrocortisone, butylated hydroxytoluene and parabens in pharmaceutical creams. J Pharm Biomed Anal., 242, 116021 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116021.
Talluri MVNK, Khatoon L, Kalariya PD, Chavan BB, Ragampeta S. LC–MS/MS characterization of forced degradation products of fidarestat: development and validation of a stability-indicating RP-HPLC method. J Chromatogr Sci., 53 (9), 1588–1596 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmv061.
Mugisho OO, Aryal J, Shome A, Lyon H, Acosta ML, Green CR, Rupenthal ID. Orally delivered connexin43 hemichannel blocker, tonabersat, inhibits vascular breakdown and inflammasome activation in a mouse model of diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci., 24 (4), 3876 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043876.
Dong MW, Huynh-Ba K, Wong A. Validation of stability-indicating HPLC methods for pharmaceuticals: overview, methodologies, and case studies. LCGC North America., 38 (11), 606–618 (2020).
Iqbal DN, Ashraf A, Iqbal M, Nazir A. Analytical method development and validation of hydrocortisone and clotrimazole in topical dosage form using RP-HPLC. Future J Pharm Sci., 6, 65 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00065-7.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Kajal Sunil Shinde, Chandraprabhu Motichand Jangme, Abhinandan Raosaheb Patil

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















